之前学 swift3 顺带整理的小笔记
Objective-C
介绍
| 文件后缀 |
文件类型 |
*.h |
头文件。头文件包含类,类型,函数和常数的声明。 |
*.m |
源代码文件。这是典型的源代码文件扩展名,可以包含 Objective-C 和 C 代码 |
*.mm |
源代码文件。带有这种扩展名的源代码文件,除了可以包含Objective-C和C代码以外还可以包含C++代码。仅在你的Objective-C代码中确实需要使用C++类或者特性的时候才用这种扩展名。 |
说明
| 关键词 |
说明 |
| #import |
引入文件, 并确保相同的文件只会被包含一次 |
| NSString* say = @”Hello World” |
创建NSString对象 |
| @interface/@implementation |
objective-c 一个类是由:定义和实现来构成的, @interface 用于定义, @implementation用于实现细节. |
| @property与@synthesize |
@property用于在@interface声明getter与setter函数, @synthesize用于在@implementation实现getter与setter函数,
二者是搭配口味
高版本(Xcode4.5)可省略@synthesize |
基础框架
<Foundation/Foundation.h>
- 它包括 NSArray,NSDictionary中的NSSet等扩展数据类型的列表。
- 它由一组丰富的操作文件的函数,字符串,等等。
- URL处理它提供的功能,如日期格式,数据处理,错误处理等实用工具
语法
语法速读
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| /* 预处理(导包) */
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
/* 定义接口(继承:NSObject) */
@interface SampleClass:NSObject
- (void)sampleMethod;
@end
/* 实现接口(SampleClass) */
@implementation SampleClass
- (void)sampleMethod{
NSLog(@"Hello, World!
");
}
@end
/* 主函数 */
int main() {
/* my first program in Objective-C */
SampleClass *sampleClass = [[SampleClass alloc]init];
/* - 调用函数
C: sampleClass.sampleMethod(args);
OC: [对象 函数名: 参数]
*/
[sampleClass sampleMethod: args];
return 0;
}
|
类的语法
类分为: 类的定义(.h) 和 类的实现(.m)
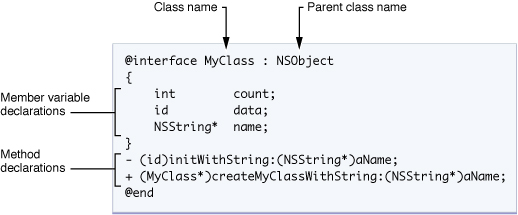
定义 ( *.h )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| @interface MyObject : NSObject
{
// 此处变量默认为受保护(protected)
int memberVar1; // 实体变量
id memberVar2;
}
+(return_type) class_method; // "+" 表示 类方法
-(return_type) instance_method1; // "-" 表示 实例方法
-(return_type) instance_method2: (int) p1;
// 这里的调用方式为: [obj instance_method3: 1 andPar: 2];
// andPar 相当于外部的另外一个别名
-(return_type) instance_method3: (int) p1 andPar: (int) p2;
@end
|
实现 ( *.m )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| @implementation MyObject
{
// 此处变量为私有(private)
int memberVar3; //私有实体变量
}
+(return_type) class_method {
.... //method implementation
}
-(return_type) instance_method1 {
....
}
-(return_type) instance_method2: (int) p1 {
....
}
-(return_type) instance_method3: (int) p1 andPar: (int) p2 {
....
}
@end
|
创建对象
1
2
3
4
| // 注: alloc 与 init 都属于 NSObject 里的函数
MyObject * my = [[MyObject alloc] init];
// 无参构建, 也可采用以下方式 (Objective-C 2.0)
MyObject * my = [MyObject new];
|
Note: { } 需如文这样标识, 才可表达出准确的语义, 读者自行领悟.
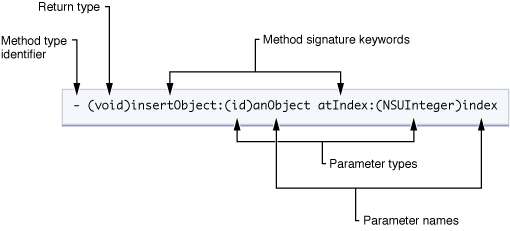
函数语法
函数分为: 类函数 和 对象函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| // 如上
// 定义语法: 范围标识 (返回值)函数名:外部形参别名:(参数类型) 形参名 外部形参别名:(参数类型) 形参名
// 注: 第一个 外部形参别名 可省略
- (void)insertObject:(id)anObject atIndex:(NSUInteger) index
+ (void)insertObject:(id)anObject atIndex:(NSUInteger) index
// 调用
// 对象调用 [对象 函数名: 参数1 外部形参别名: 参数2]
[obj insertObject: arg1 atIndex: arg2]
// 类调用 [类名 函数名: 参数1 外部形参别名: 参数2]
[Object insertObject: arg1 atIndex: arg2]
// 注:) 类调用 和 对象调用 的形式是一样的
|
属性语法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| @interface Person : NSObject
{
/*
相当于 @public 至 @private 之间的属性被暴露出去
可通过实例直接访问, 例如: obj->name
*/
@public
NSString *name;
@private
int age;
}
/*
参考: http://justcoding.iteye.com/blog/1444548
使用范围: @interface, @protocol, @category
可声明特性:
读写属性: (readwrite/readonly)
setter语意:(assign/retain/copy)
原子性: (atomicity/nonatomic)
使用效果(声明一个setter与getter方法):
- (NSString*)name;
- (void)setName: (NSString*)newName;
*/
@property(copy) NSString *name;
@property(readonly) int age;
-(id)initWithAge:(int)age;
@end
@implementation Person
/*
使用范围: @implementation
使用效果(自动实现一个setter与getter方法):
- (NSString*)name {
return name;
}
- (void)setName: (NSString*)newName {
name = newName;
}
*/
@synthesize name;
/* @dynamic 仅仅是告诉编译器这两个方法在运行期会有的,无需产生警告 */
@dynamic age;
-(id)initWithAge:(int)initAge
{
age = initAge; // 注意:直接赋给成员变量,而非属性
return self;
}
-(int)age
{
return 29; // 注意:并非返回真正的年龄
}
@end
|
类或协议的属性可以被动态的读取
类似反射机制 , 略过..
快速枚举
一种省内存的循环遍历 , 略过..
协议语法
类似 Java 中的接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| /*定义协议*/
@protocol Locking
- (void)lock;
- (void)unlock;
@end
/*
类的@interface 宣称使用 协议
*/
@interface SomeClass : SomeSuperClass <Locking>
@end
/*
类的@implementation 实现 协议 细节
*/
@implementation SomeClass
- (void)lock {
// 实现lock方法...
}
- (void)unlock {
// 实现unlock方法...
}
@end
|
动态类型
id 相当于 Java 中的 Object, 即 任意对象
类别 (Category) 语法
分类不仅可以增加类的方法,也可以代替原有的函数, 并不能新增变量
动态增加和替换函数, 强得一匹
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
/*
说明: 定义扩展 Integer类 接口, 新增/覆盖 函数 showstars 与 showint
语法:
#import "待扩展类接口文件.h"
@interface 待扩展类(扩展类)
// 函数定义
@end
*/
#import "Integer.h"
@interface Integer(Display)
- (id) showstars;
- (id) showint;
@end
/*
说明: 实现扩展 Integer类 接口, 新增/覆盖 函数 showstars 与 showint
语法:
#import "扩展类接口文件.h"
@implementation 待扩展类(扩展类)
// 函数实现
@end
*/
#import "Display.h"
@implementation Integer(Display)
- (id) showstars {
..
}
- (id) showint {
..
}
@end
|
NOTE: 使用时需#import 待扩展类与扩展类的接口文件**(.h)**
划重点
NSString*/NSObject*等 表示对象self 某种程度相当于 this- nil 基本上等同于 NULL
- 调用属性 self->name
- 一般(.h 存放**@interface文件**, .m 存放**@implementation文件**). 进行#import时, 只需#import .h文件

